Progress 进度条
例子#
基本用法#
export function App() { return ( <Window> <DemoLayout> <Progress value={75} max={100} animation></Progress> </DemoLayout> </Window> );}
interface IDemoLayoutProps { children?: any[] | any; width?: string; height?: string;}
function DemoLayout(props: IDemoLayoutProps) { const width = props?.width ?? '240dpx'; const height = props?.height ?? '32dpx';
const demoLayout = { columns: `1 ${width} 1`, rows: `1 ${height} 1`, areas: { center: { row: 1, column: 1 }, }, }; return ( <Grid style={{ layout: demoLayout }}> <Grid style={{ area: demoLayout.areas.center }}> {props.children} </Grid> </Grid> );}在这个例子中,我们演示了进度条的基本用法:
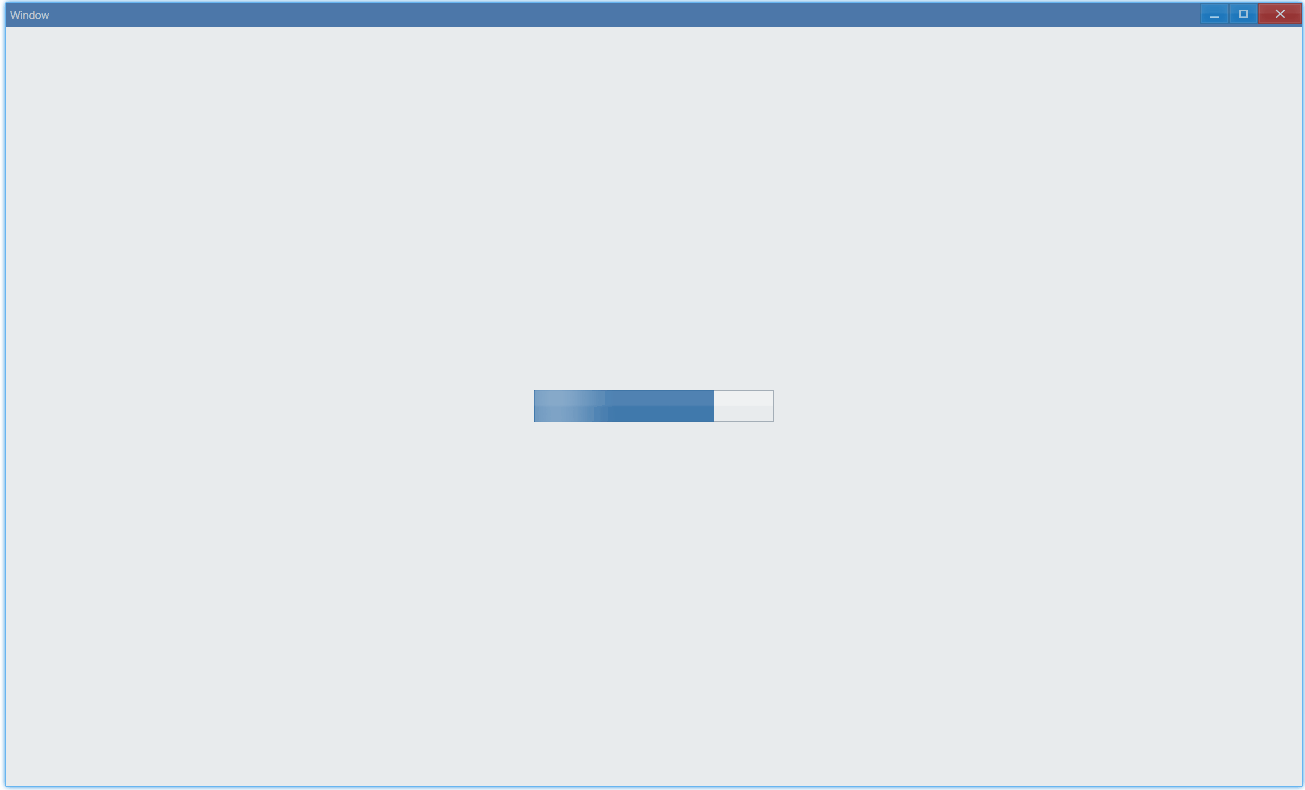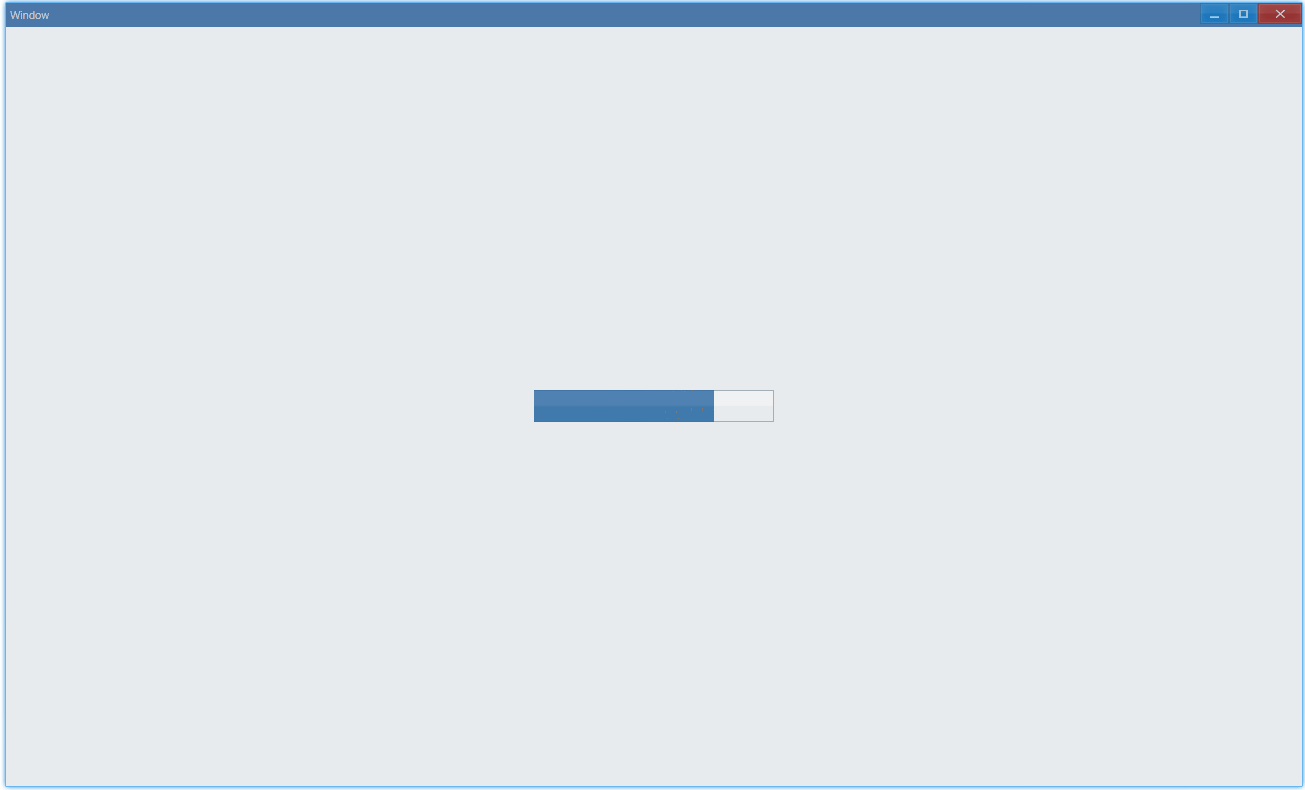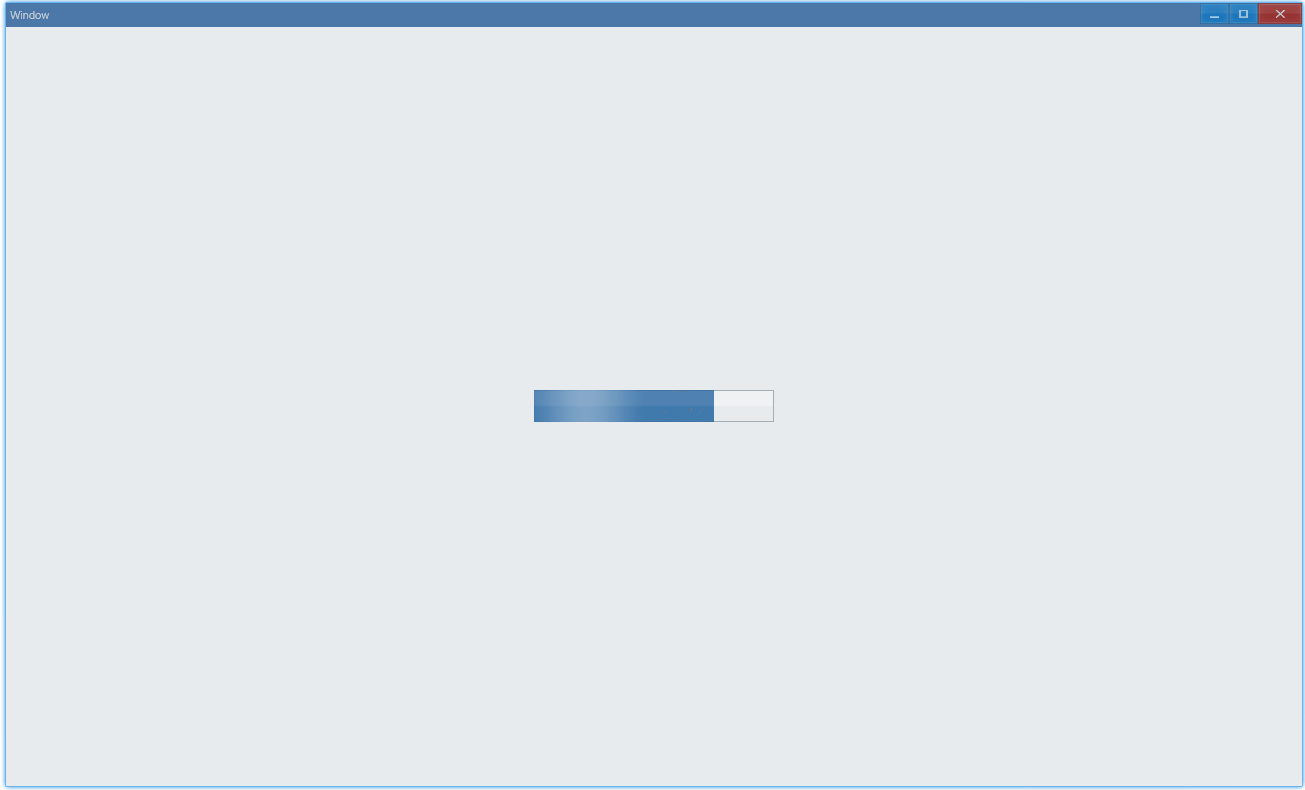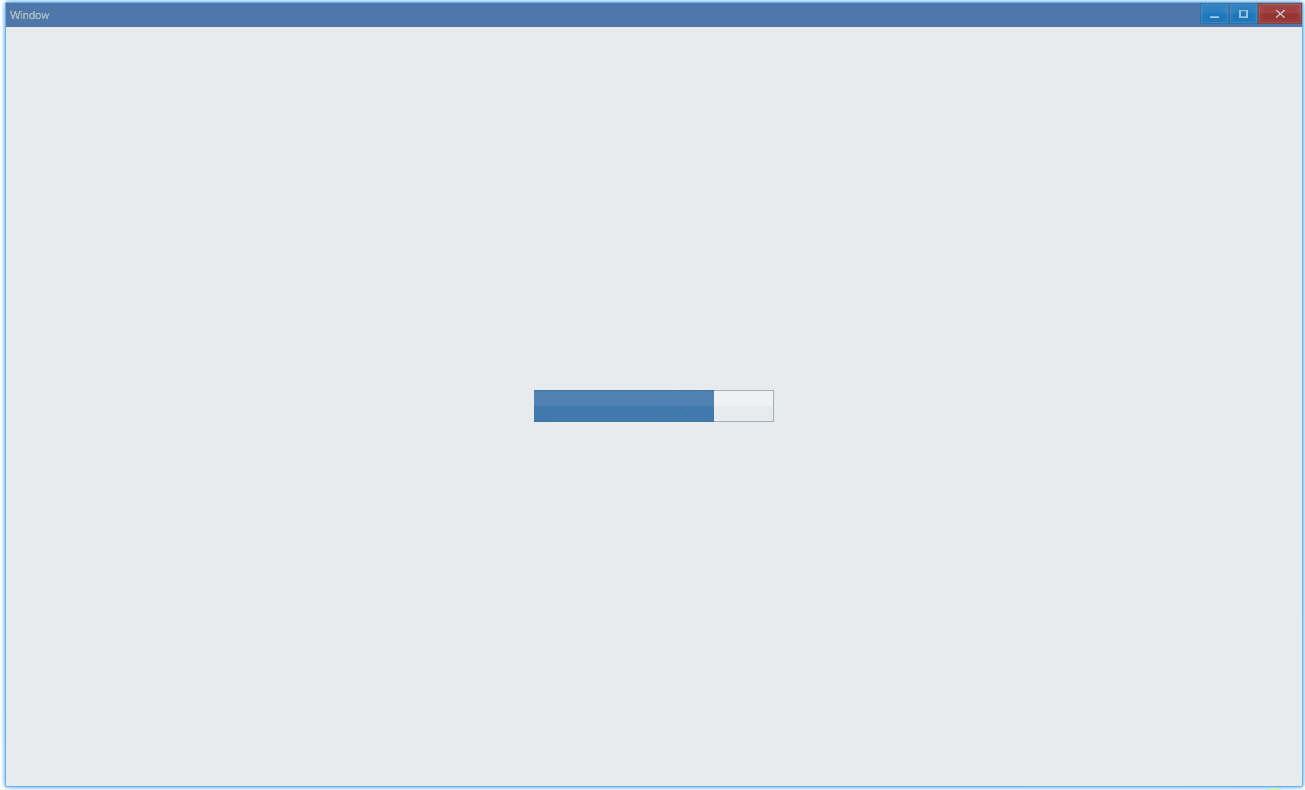
其中animation设置的动画是进度条中光影的流动。
API#
export interface IProgressComponentProps extends IComponentProps { value: number; max?: number; animation?: boolean;}状态#
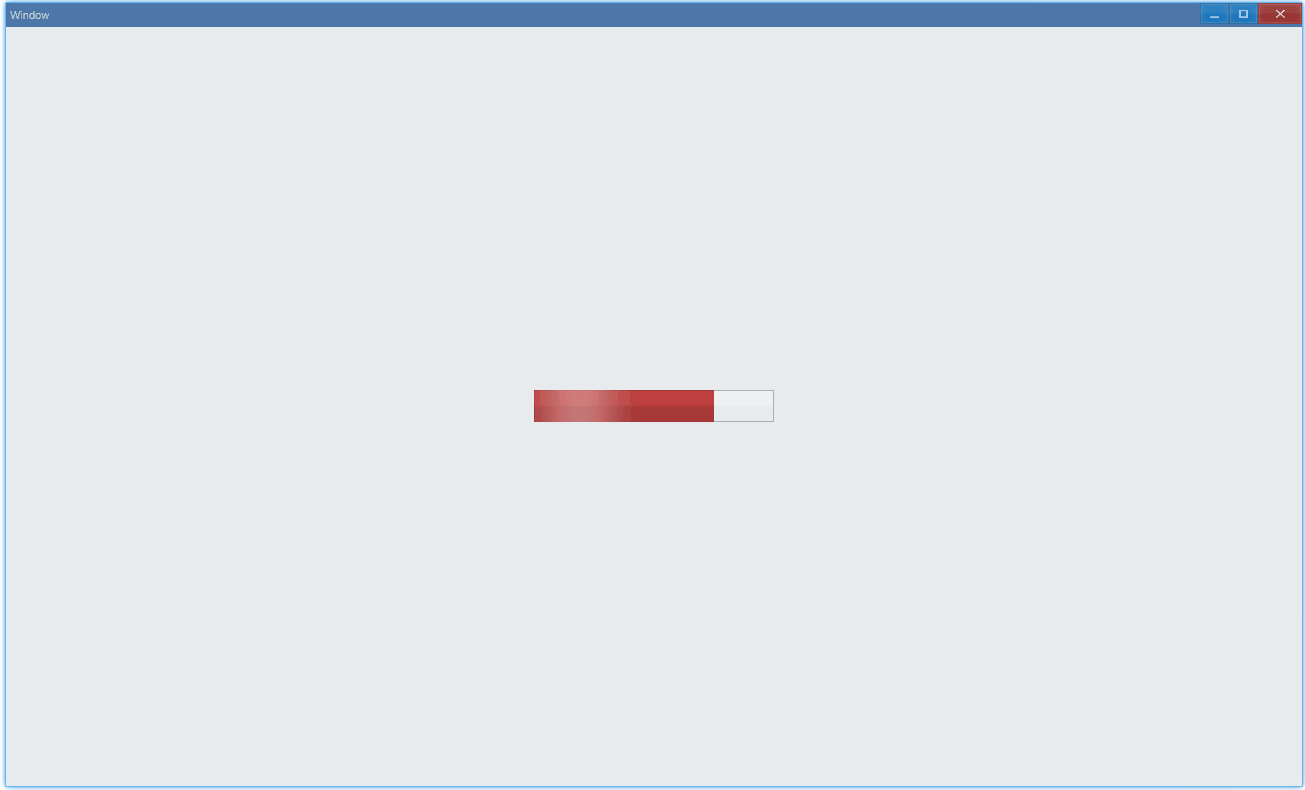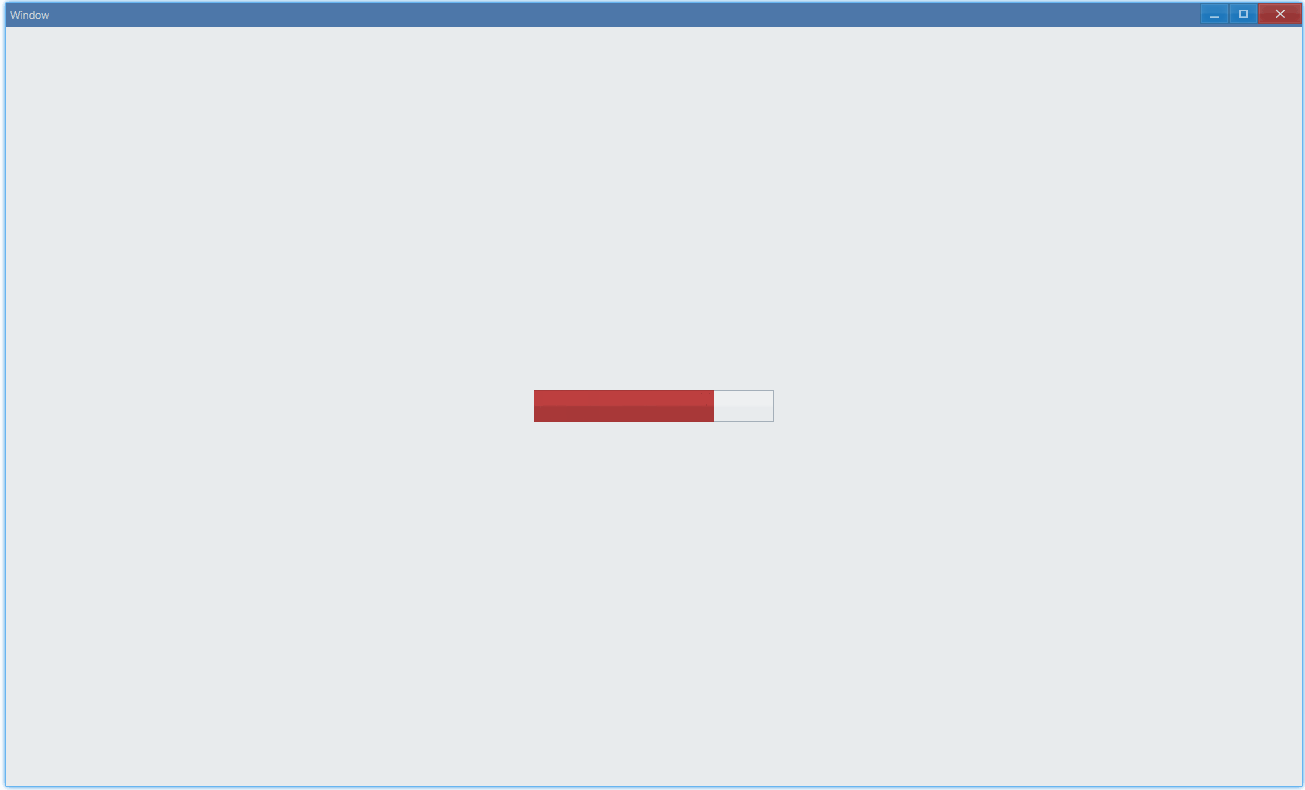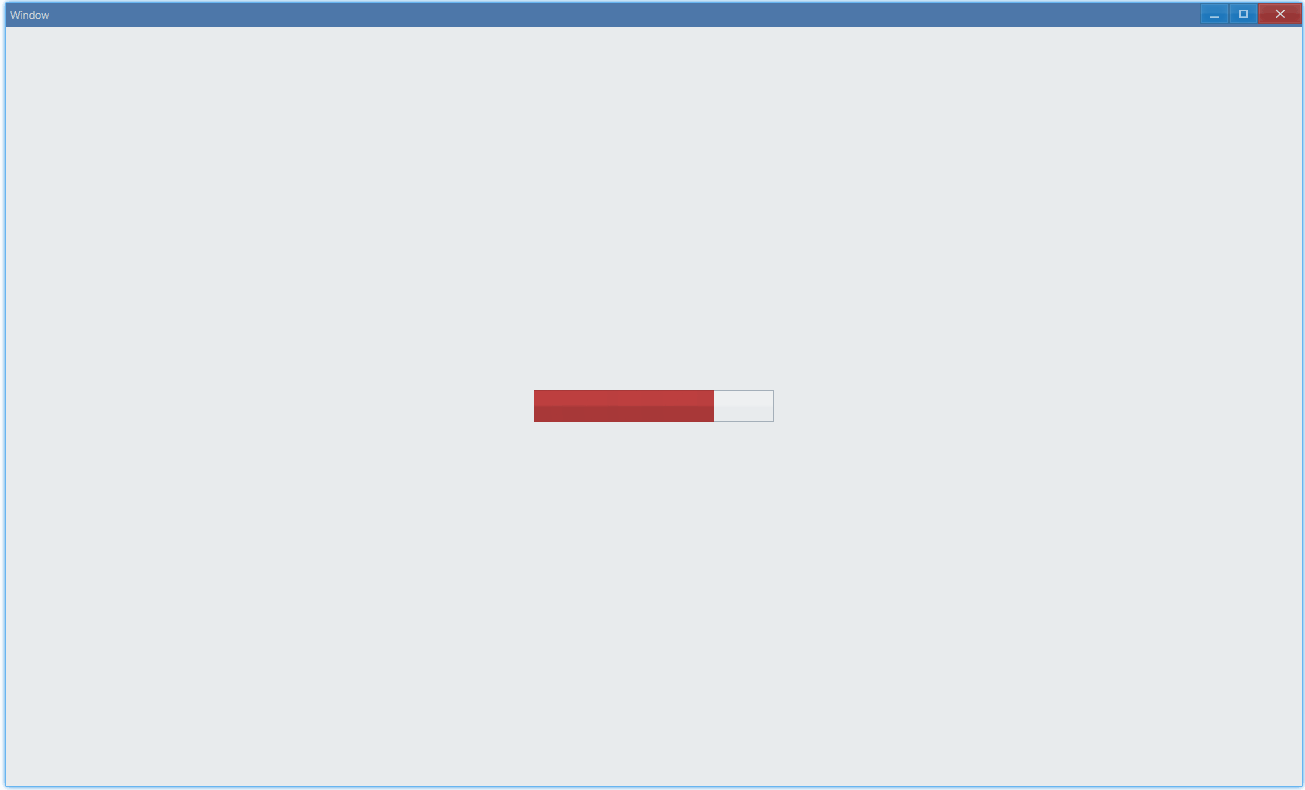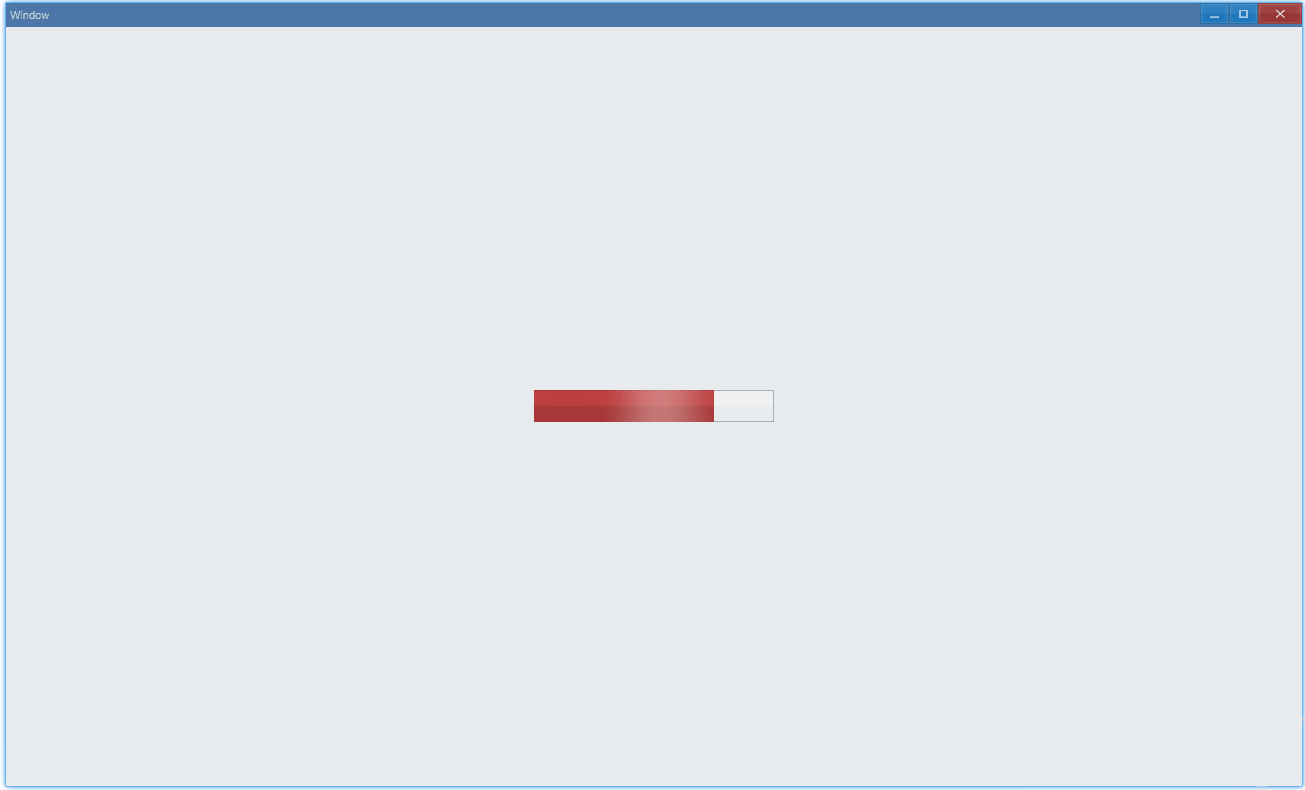
通过 state 可以设置进度条状态:
export function App() { return ( <Window> <DemoLayout> <Progress value={75} max={100} animation state={ProgressBarState.Normal} ></Progress> </DemoLayout> </Window> );}- Normal
- Paused
- Error
- Pulse



API#
export interface IProgressBar extends IControl { SetState(state: ProgressBarState): ProgressBar; GetState(): ProgressBarState;}
export enum ProgressBarState { Normal, Paused, Error, Pulse, None,}步长(每次增加多少)#
export function App() { const [value, setValue] = useState(0); useEffect(() => { setInterval(() => { if (value < 100) { setValue((prev) => prev + 1); // step is 1 } }, 100); }, []); return ( <Window> <DemoLayout> <Progress value={value}></Progress> </DemoLayout> </Window> );}这个例子演示了怎样实现通常我们看到的“进度条不断增长”的效果: